Softmax-with-Loss
크로스 엔트로피를 손실함수로 사용하는 Softmax 계층이다.
계산 그래픈느 다음과 같다.
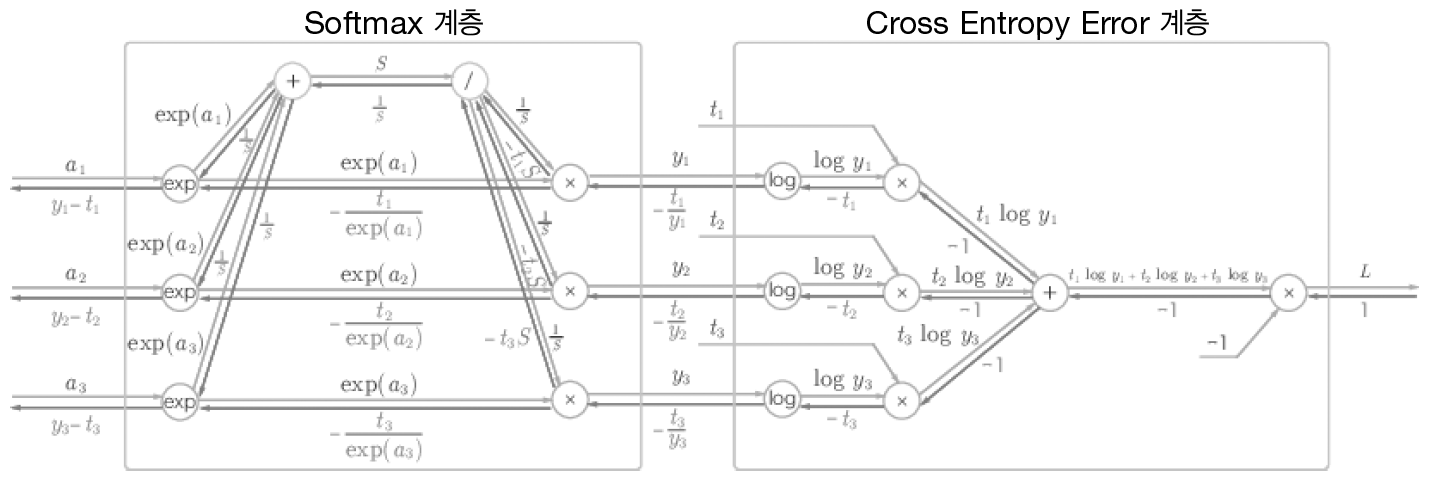
복잡해 보이지만 뒤에서부터 차근차근 이해하면 어렵지 않다.
결론적으로 이 계층의 역전파 결과는 $Y-T$로 깔끔하게 떨어진다. 이러한 부분이 오차역전파가 계산량을 획기적으로 줄여주는 이유이다. 책에서는 이러한 결과가 우연이 아니고 크로스 엔트로피라는 함수가 이렇게 설계되었다고 한다.
이를 클래스로 구현해보자
class SoftmaxWithLoss:
def __init__(self):
self.loss = None
self.y = None
self.t = None # (one-hot)
def forward(self, x, t):
self.t = t
self.y = softmax(x)
self.loss = cross_entropy_error(self.y, self.t)
return self.loss
def backward(self, dout=1):
batch_size = self.t.shape[0]
if self.t.size == self.y.size: # t가 one-hot인 경우
dx = (self.y - self.t) / batch_size
else:
dx = self.y.copy()
dx[np.arange(batch_size), self.t] -= 1
dx = dx / batch_size
return dxbackward 부분에서 역전파가 y - t이므로 t에 해당하는 index만 1을 빼주는 것이다. 그리고 batch_size로 나눠서 데이터 1개당 오차를 앞 계층으로 전파한다.
오차역전파법 구현하기
앞에서 구현한 계층들을 블록 조립하듯이 조립하여 신경망을 구축할 수 있다.
class TwoLayerNet:
def __init__(self, input_size, hidden_size, output_size, weight_init_std=0.01):
# 가중치 초기화
self.params = {}
self.params['W1'] = weight_init_std * np.random.randn(input_size, hidden_size)
self.params['b1'] = np.zeros(hidden_size)
self.params['W2'] = weight_init_std * np.random.randn(hidden_size, output_size)
self.params['b2'] = np.zeros(output_size)
# 계층 생성
self.layers = OrderedDict() # 딕셔너리에 추가한 순서를 기억함
self.layers['Affine1'] = Affine(self.params['W1'], self.params['b1'])
self.layers['Relu1'] = Relu()
self.layers['Affine2'] = Affine(self.params['W2'], self.params['b2'])
self.lastLayer = SoftmaxWithLoss()- OrderDict() 을 사용하여 딕셔너리에 추가한 순서를 기억할 수 있다. 이렇게 하면 value들을 하나씩 불러와 간편하게 forward 혹은 backward를 수행할 수 있다.
- SoftmaxWithLoss() 계층을 따로 저장하는 이유는 predict 할 때 필요 없기 때문이다.
def predict(self, x):
for layer in self.layers.values():
x = layer.forward(x)
return x
def loss(self, x, t):
y = self.predict(x)
return self.lastLayer.forward(y, t)
def accuracy(self, x, t):
y = self.predict(x)
y = np.argmax(y, axis=1)
if t.ndim != 1: # 정답 레이블이 one-hot인 경우
t = np.argmax(t, axis=1)딱히 설명할 것이 없다.
def gradient(self, x, t):
# forward
self.loss(x, t)
# backward
dout = 1
dout = self.lastLayer.backward(dout)
layers = list(self.layers.values())
layers.reverse()
for layer in layers:
dout = layer.backward(dout)
grads = {}
grads['W1'], grads['b1'] = self.layers['Affine1'].dW, self.layers['Affine1'].db
grads['W2'], grads['b2'] = self.layers['Affine2'].dW, self.layers['Affine2'].db
return grads오차역전파를 이용해 gradient를 구한다. 학습할 때 이 메서드를 사용해 gradient를 구하고 가중치 매개변수를 갱신한다.
학습 구현은 중요한게 아니라서 생략!
'책 > 밑바닥부터 시작하는 딥러닝' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 6장 학습 관련 기술들 (2) (0) | 2023.09.20 |
|---|---|
| 6장 학습 관련 기술들 (1) (0) | 2023.09.20 |
| 5장 오차역전파법 (1) (0) | 2023.09.19 |
| 4장 신경망 학습 (2) (0) | 2023.09.14 |
| 4장 신경망 학습 (1) (0) | 2023.09.13 |


